Asustor AS5102T Manual
Læs nedenfor 📖 manual på dansk for Asustor AS5102T (109 sider) i kategorien I DEN. Denne guide var nyttig for 8 personer og blev bedømt med 4.5 stjerner i gennemsnit af 2 brugere
Side 1/109

User Guide
For Network Attached Storage
Ver.2.5. (For ADM 2.5) 1214

3
AiData ................................................................................................................................... 92
AiMaster ................................................................................................................................. 93
AiRemote ............................................................................................................................... 94
AiDownload ............................................................................................................................ 95
AiMusic .................................................................................................................................. 96
AiFoto .................................................................................................................................... 97
AiVideos ................................................................................................................................. 98
AiSecure ................................................................................................................................ 98
Appendix ....................................................................................................
99
Permission Mapping Table ........................................................................................................ 99
EULA
........................................................................................................ 100 8.
GNU General Public License
......................................................................... 102

4
Introduction 1.
Thank you for choosing ASUSTOR network attached storage (NAS).
From cross-platform file sharing to multimedia server applications to App Central, ASUSTOR NAS
provides you with a rich assortment of features, allowing you to explore the unlimited potential of NAS.
ADM: The Amazing Starts Here
Your NAS comes preloaded with , an operating system developed by ASUSTOR Data Master (ADM)
ASUSTOR. Designed around the use of Apps, ADM s intuitive web-based interface allows for easy ’
organization and a user-friendly experience. This user manual will introduce you to all the rich
assortment of preloaded applications (Apps) on your NAS.

5
Your Ideal Private Cloud
ASUSTOR s exclusive Cloud Connect’TM technology lets you access your NAS from almost anywhere on
the planet. Whether by computer or mobile device you need only an Internet connection to access
your NAS from anywhere and at any time.
Cross-Platform File Sharing
ASUSTOR NAS provides flawless cross-platform file sharing. No matter what operating system you
are using, you can still effortlessly connect to your NAS and access your data.
Embrace the Cloud, Enjoy Peace of Mind
Experience the convenience of cloud computing in a stress free environment. ASUSTOR s ADM ’
Defender and support for encryption provide the highest standard of security for your system.
Your Data is Safe with Us
ASUSTOR NAS offers a complete host of data protection and backup solutions. Features such as RAID
and two-way transfer support offer bullet-proof protection and flexible application. Savor a stress free
and liberating user experience.

6
The Hub of Your Home Entertainment
Make ASUSTOR NAS the hub of your home entertainment and enjoy digital entertainment like you
never have before. Countless Apps such as ASUSTOR Portal, XBMC, Kodi, LooksGood, SoundsGood,
Photo Gallery, iTunes Server and UPnP AV Multimedia Server allow you to enjoy digital entertainment
in every corner of your home.
Vigilant Security
ASUSTOR s Surveillance Center lets you collectively manage an array of IP cameras, helping you ’
keep an eye on your most valued assets. You can even take snapshots and control the pan, tilt and
zoom functions of all cameras. In the event of any disruptions, Surveillance Center will notify you at
once, giving you complete peace of mind.

7
iSCSI and Virtualization
Seamlessly integrate with any existing IT environments. Enjoy flexible and cost-efficient shared
storage. ASUSTOR NAS supports the use of iSCSI and NFS in addition to being verified as, Citrix and
Hyper-V ready.
Protect Our Planet with ASUSTOR
It is our mission to continue to develop exceptionally energy efficient products. From their inception,
all ASUTOR NAS products are designed and developed around ecologically friendly concepts. Features
such as, Night Mode, disk hibernation, power scheduling and fan control all help you to save power.
Furthermore, each ASUSTOR NAS is fully compliant with EuP standards (EuP 2.0).

8
Enrich Your Mobile Life
Imagine having your photos, media files and important documents always at your fingertips.
ASUSTOR offers an array of mobile applications to make your digital lifestyle complete.
App Central: Unleash the Unlimited Potential of NAS
The Apps that come pre-installed with ASUSTOR NAS are just the beginning. At your convenience,
browse through and download any additional Apps that peak your interest from App Central. Explore
the unlimited potential of ASUSTOR NAS while creating a personalized NAS for yourself.
Online Resources
Forum (English): http://forum.asustor.com
Downloads: http://www.asustor.com/service/downloads
Technical Support: http://support.asustor.com
Terms of Use
All ASUSTOR products have undergone stringent and comprehensive testing. Under normal user
operation and within the warranty period, ASUSTOR will assume responsibility for any hardware
failures. Before using this product, please read the End-User License Agreement (EULA) located at the
end of this user manual.

9
Getting Started with ASUSTOR Data Master 2.
This section will introduce you to the process of logging in, using Searchlight and using the
taskbar in ASUSTOR Data Master (ADM).
Installing ASUSTOR NAS and ADM
Before you begin using your NAS, please make sure that you have installed hard disks, connected the
NAS and have properly initialized it. For detailed instructions on setting up your ASUSTOR NAS and
installing ADM, please see the for your ASUSTOR NAS model. ThQuick Installation Guide e Quick
Installation Guide may be found on the Installation CD that came with your NAS or downloaded from
the Downloads section of the ASUSTOR website (http://www.asustor.com/service/downloads).

10
Logging in to ASUSTOR Data Master
After installation and initialization, you can use the following methods to log in to your ASUSTOR NAS:
Use ASUSTOR Control Center to scan your local area network for ASUSTOR NAS devices. Select
your NAS and then click on the button to go to bring up the login screen. “Open”
If you already know the IP address for your ASUSTOR NAS on your local area network, you can
directly enter it into your web browser to connect to your NAS. For example:
http://172.16.1.69:8000/
If you are connecting to your ASUSTOR NAS remotely, you can enter your personalized hostname
into your web browser to connect to your NAS. For example: http://john.myasustor.com:8000
Reminder: When connecting remotely, please remember to register your NAS and then
enable Cloud Connect under [Settings [Ease of Access] [Cloud Connect] [Enable ] → → →
Cloud Connect].
After configuring a Cloud ID for your NAS, you will be able to connect to it remotely using your
customized hostname.

11
Searchlight
Developed by ASUSTOR, Searchlight is a rapid search technology that is built into ADM and provides
quick and precise searches allowing you to easily find the files that you need. After logging in to ADM
you will be able to find Searchlight’s magnifying glass icon on the taskbar in the upper right-hand
corner of the screen.
Taskbar
The ADM taskbar allows you to directly [Pin to taskbar], [Restore], [Minimize], [Close] any Apps that
are on it. In the [Account] menu you will see items for [Settings], [Sleep], [Restart], [Restart], [Shut
down] and [Sign out].activity

12
Selecting [Settings] will provide you with tabs for [Personal], [Volume Usage] and [Home Screen].
Personal: Here, you can configure the account password, E-mail address, description and ADM
language.
Volume Usage: Here, you can view information regarding your hard disk storage volumes such
as usage and storage quota.
Home Screen: Here you can upload images to the NAS or select an image from the NAS to
customize your desktop. You can also customize the ADM text colors, position of desktop
wallpaper and remove desktop wallpaper.

13
Pre-Installed Apps 3.
Pre-installed Apps include the configuration of function and service settings for hard disks and
hardware. You can configure everything from system related settings to user access rights.
Settings
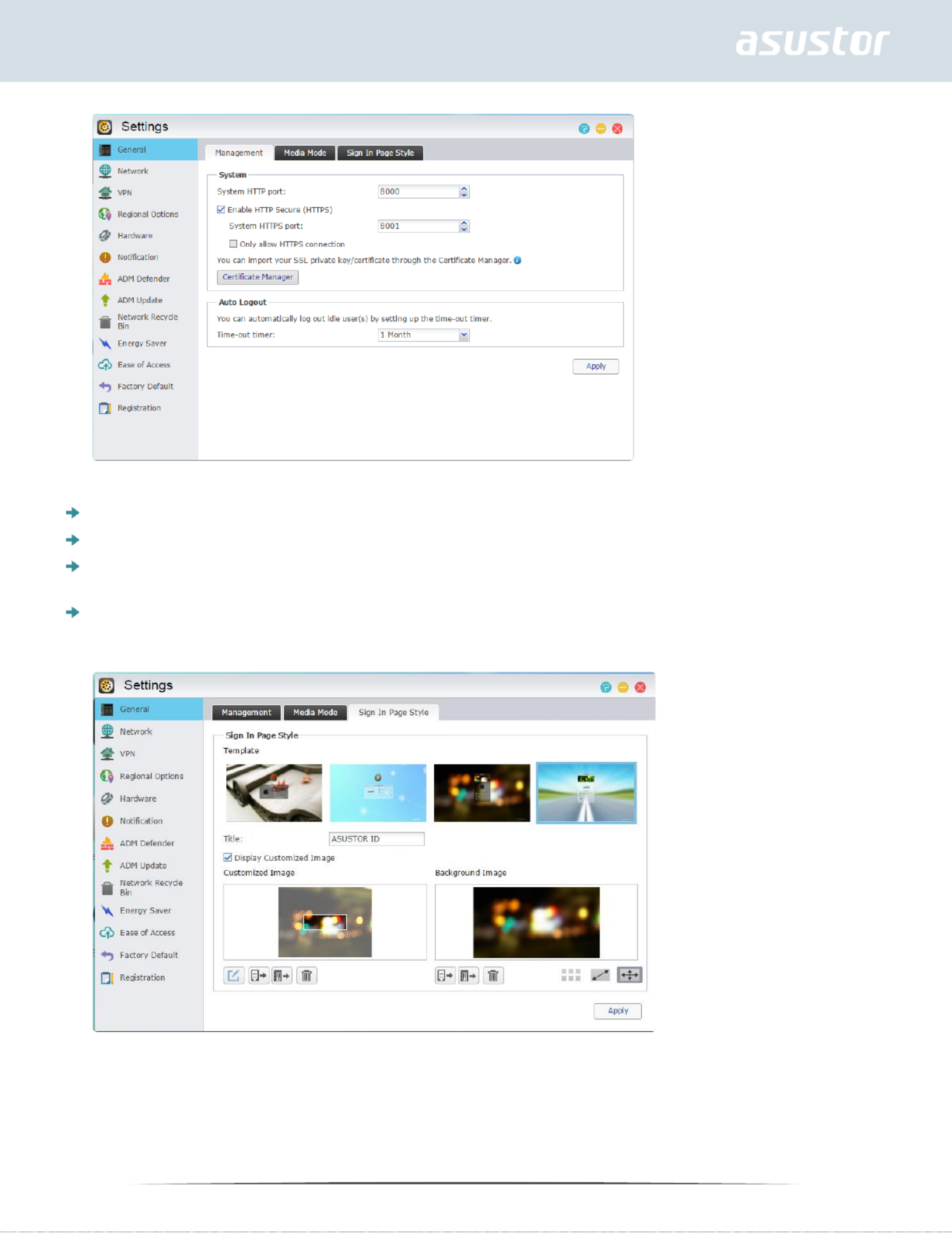
General
Here you can manage the system HTTP port and auto logout settings. Auto logout will logout users if
they remain idle past the specified period of time.
System HTTP Port: This is used to specify the port you wish to use to connect to ADM’s web
based user interface. You can access your NAS by opening a web browser and entering your IP
address followed by a colon and the specified port number.
For example: http://192.168.1.168:8000
Timeout timer: For security concerns, users that remain idle past the specified period of time
after logging on will be automatically logged off.
14
Sign in page: Under Sign In Page Style you will be able to configure the following:
Sign In Page Title: The text entered here will be displayed on the sign in page.
Sign In Page Background Image: Here you can change the background image of the sign in
page. The image formats currently supported are: JPG
Sign In Page Customized Image: Here you can choose to enable or disable the sign in page
customized image. Using the crop function you can configure the position and size of the
customized image. The image formats currently supported are: JPG
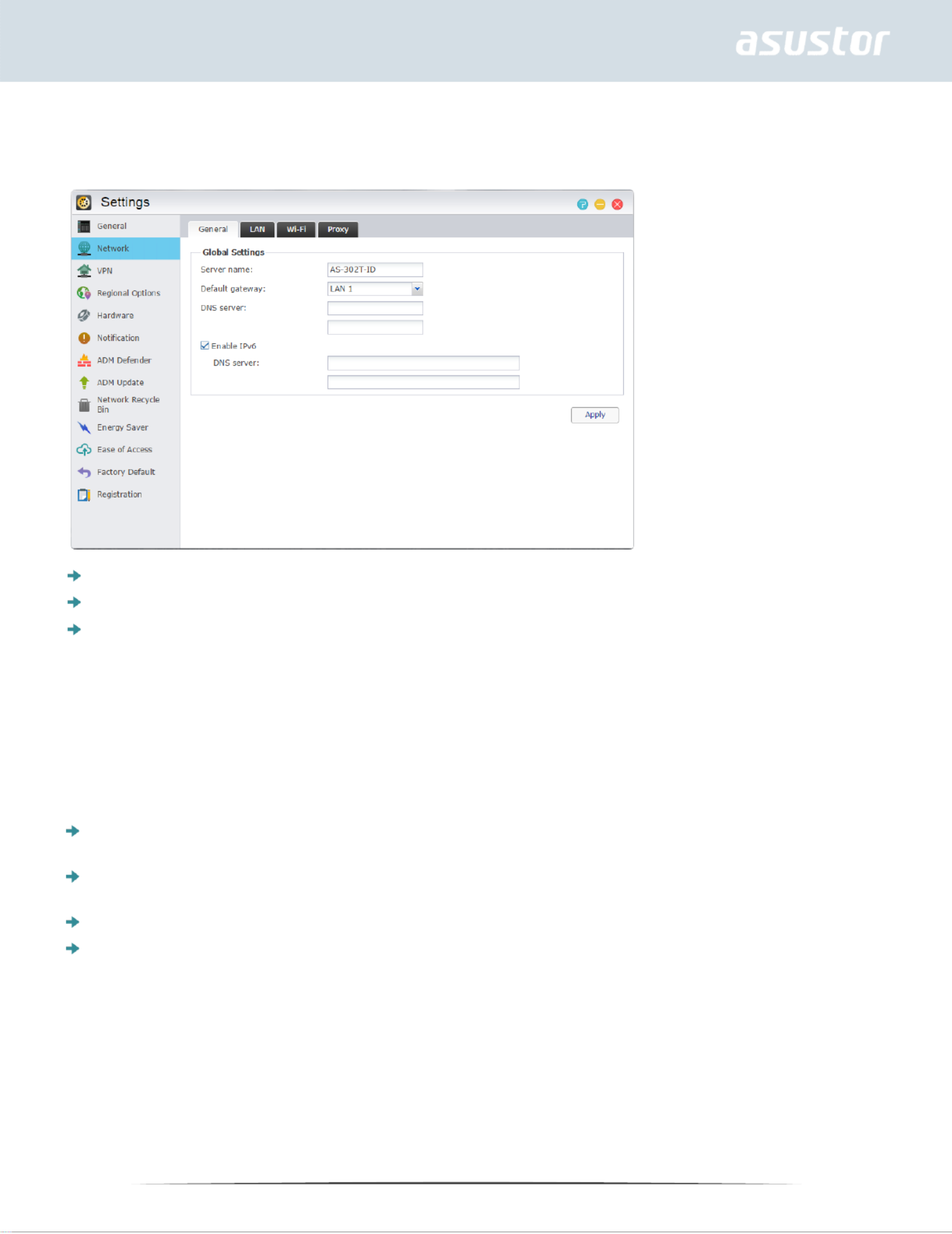
Network
15
Note: This function may differ depending on the NAS model in use.
Here you can configure the server name, LAN and Wi-Fi settings. Other settings include IP address,
DNS server and default gateway.
Server Name: An online name for your NAS.
Default Gateway: The default gateway that you wish to use.
DNS Server: Here you can set the DNS server that you wish to use. Should you choose to obtain
your IP address via DHCP the system will automatically obtain the available DNS servers for you.
If you choose to manually enter an IP address then you will have to manually enter a DNS server
as well.
Reminder: Using an invalid DNS server will affect some network related functions. (i.e.,
Download Center). If you are uncertain about how to proceed, please choose to obtain your
IP address automatically.
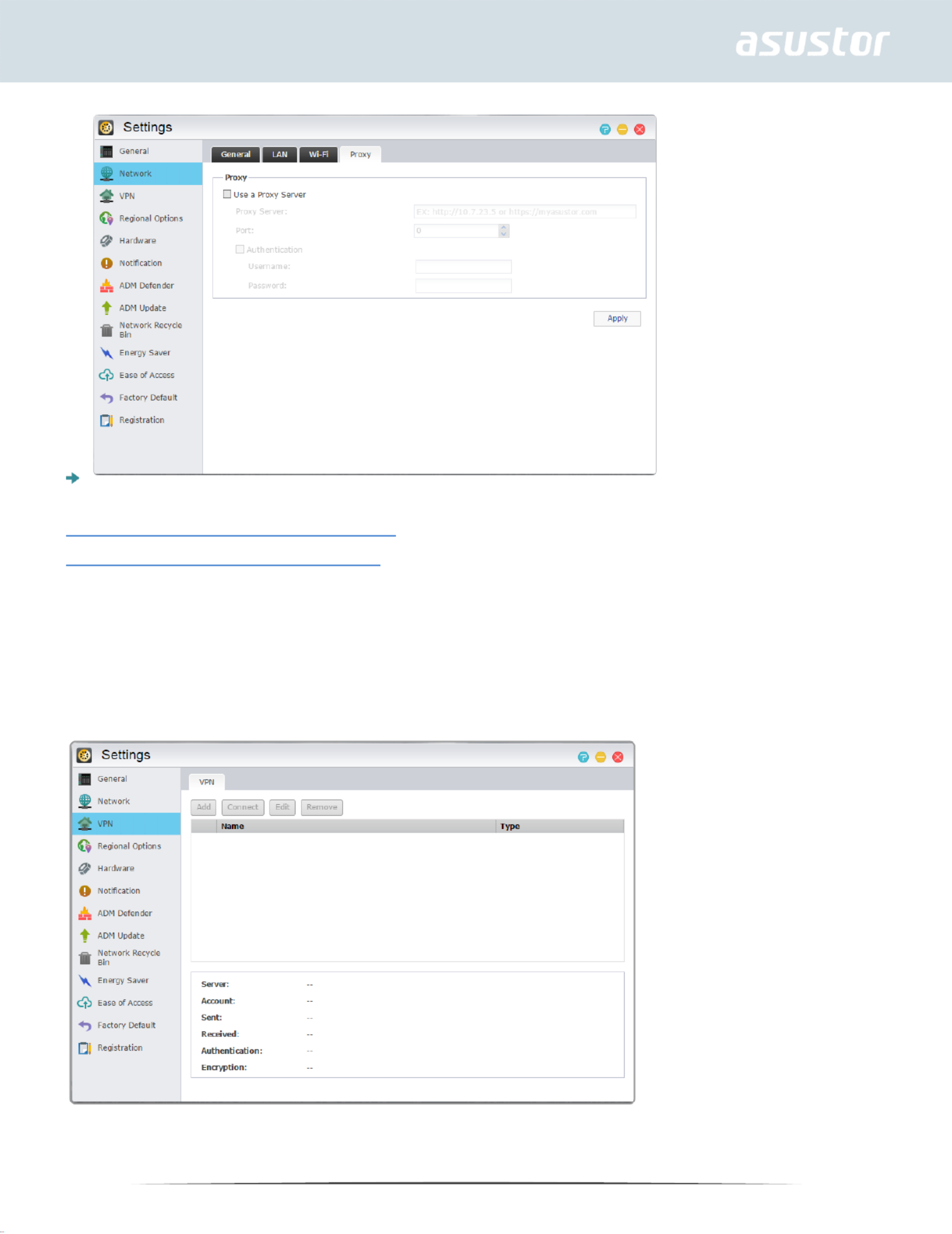
Proxy: Here you can enable proxy server connections, allowing the NAS to connect to the internet
via a proxy server.
Proxy Server: The address of the proxy server you wish to connect to. (Supports HTTP and
HTTPS)
Port: The communications port of the proxy server.
Authentication: If the proxy server you are using requires authentication, you can enable it here
and then enter your username and password.
16
See More
NAS 105 – Networking: A Beginner’s Guide
NAS 307 – Networking: Link Aggregation
VPN
Here you can let your ASUSTOR NAS become a VPN client, and via PPTP or Open VPN, connect to a
VPN server to access a virtual private network. ASUSTOR NAS supports the use of different
connection settings files, allowing you to connect to the VPN server of your choice. The ASUSTOR
VPN client currently supports the two most common connection protocols: PPTP and OpenVPN.

17
Reminder: The VPN client cannot be used simultaneously with the VPN Server. If you need
to use the VPN client, please first stop any use of the VPN server.
See More
NAS 322 - Connecting Your NAS to a VPN
Regional Options
Here you can adjust the settings for date and time, display format, time zone and daylight saving
time.
Hardware
Note: This function may differ depending on the NAS model in use.
Here you can configure settings for the LED indicators, buzzer, hard disk hibernation, power usage,
fan speed and LCD display panel.
System: Here you can choose to disable any of the LED indicators to save power. By selecting
"night mode", only the system power LED indicator will be enabled. It will flash an orange light
every 10 seconds. "Night mode scheduling" will allow you to configure the start time and duration
of night mode. You can also configure settings for the buzzer and reset button here.

18
Disk Hibernation: Your hard disks will enter hibernation mode when left idle for the period of
time specified here. Once in hibernation, the hard disk LED indicator on the front of the disk tray
will flash once every 10 seconds to indicate that the disk is hibernating. If an access error is
detected on a hard disk, the LED indicator on the front of the disk tray will be lit red.
Sleep Mode: Here you can configure the time period the NAS will remain idle before
automatically entering Sleep Mode (S3). In addition to RAM, all of the NAS’s hardware will stop
running in order to conserve energy.

19
Why won’t my ASUSTOR NAS enter into Sleep Mode (S3)?
The following services will affect the NAS’s ability to enter into Sleep Mode (S3) as they require hard
disk access while running.
Download Center, Takeasy download tasks, RSS scheduled downloads, unable to enter Sleep Mode
(S3) when subscription downloads from multimedia websites are in progress
Unable to enter into Sleep Mode (S3) when Surveillance Center is recording
Unable to enter into Sleep Mode (S3) when the following Apps are syncing:Dropbox, Google Drive,
ASUS WebStorage, BitTorrent Sync
Unable to enter into Sleep Mode (S3) when the following Apps are executing backup tasks: HiDrive,
RALUS, WonderBox, Xcloud
XBMC (available on AS-6, AS-2TE, AS-3 series), Kodi (available on AS31, 50, 51, 61, 62, 70 series)
or Boxee (available on AS-6 series) is installed.
Power: Here you can manage power usage settings such as Wake- -LAN (WOL) and power On
scheduling.
Fan Control: Here you can set the rotation speed for the fan. If you are not sure about which
speed to select, you can simply select Auto. This will automatically adjust the fan speed in
accordance with the temperature of the system.

20
LCD Panel: You can have the LCD panel display a customized scrolling message or the local
temperature. This function is only available on the following models: AS-604T, AS-606T, AS-608T.
Reminder If you choose to display the local temperature, the system will use your current :
IP address to determine the temperature at your present location. The results of this may
vary, depending on your exact location.
Reset Button

22
Receive: Here you can set up the accounts that will be used to receive e-mail and SMS
notifications. You can also set the type of system notifications that will be received by these
accounts.
Push Notification: Here you can enable the push notification setting for the AiMaster mobile app
which can be downloaded from the Apple App Store or Google Play. When designated system events
occur, your ASUSTOR NAS will immediately send notification to the Apple/Google push notification
server which will then forward it to your mobile device.

23
About Push Notification
If you wish to use this feature, you must first install AiMaster on your mobile device and enable push
notifications on the device. Currently, AiMaster is available for both iOS and Android devices.
•Supports iOS 5.0 and onwards
•Supports Android 2.2 and onwards
Downloading AiMaster
In order to download AiMaster please open the App Store (for Apple devices) or Google Play (for
Android devices) on your mobile device and search for the keywords “asustor” and “AiMaster”.
Warning: Push notifications are transmitted to your device from Apple/Google’s push
notification servers. A poor Internet connection or abnormalities in Apple/Google’s push
notification service could potentially prevent AiMaster from correctly receiving notifications.

24
ADM Defender
ADM Defender can protect your NAS from malicious Internet attacks, ensuring the security of your
system.
Firewall: Here you can block specific IP addresses or only allow specific IP addresses to access
your NAS.
Trusted List: The IP(s) specified in the trusted list will not be blocked by the black list or after
multiple failed login attempts.

25
Auto Black List: After enabling this function, the client IP address will be blocked if there are too
many unsuccessful login attempts within the specified time period.
Black and White List: The Black and White list can be defined using IP address, range, and
geolocation. If you wish to define the Black and White list using geolocation, please first install the
Geo IP Database App.
About the Black and White List
The Black and White List can protect you from malicious attacks and prevent hackers from trying to
access your NAS. Supported protocols are as follows:
ADM system login (HTTP & HTTPS)
Windows File Service (CIFS/SAMBA)
Apple Filing Protocol (AFP)
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Secure Shell (SSH)
ADM Update
Here you can obtain the latest version of ADM to ensure system stability and to upgrade software
features.
Live Update: After enabling Live Update, the system will notify you of any available updates
when you log in to ADM.
Manual Update: You can go to ASUSTOR’s official website http://www.asustor.com to download
the latest version of ADM.
Network Recycle Bin

26
In order to enable the Network Recycle Bin for specific shared folders, please select “Access Control”
> “Shared Folders”, and then select the desired shared folder. Next, click on the “Edit” button to
configure it.
The configurations made on the “Recycle Bin” and “Empty Recycle Bin” tabs will be applied to all
enabled Network Recycle Bins.
About Network Recycle Bin
After enabling Network Recycle Bin, all files deleted via the following protocols will be moved to the
Recycle Bin.
Windows File Service (CIFS/SAMBA)
Apple Filing Protocol (AFP)
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
File Explorer
WebDAV
Energy Saver
Energy Saver can help you to reduce power consumption when your NAS is inactive or being lightly
used.
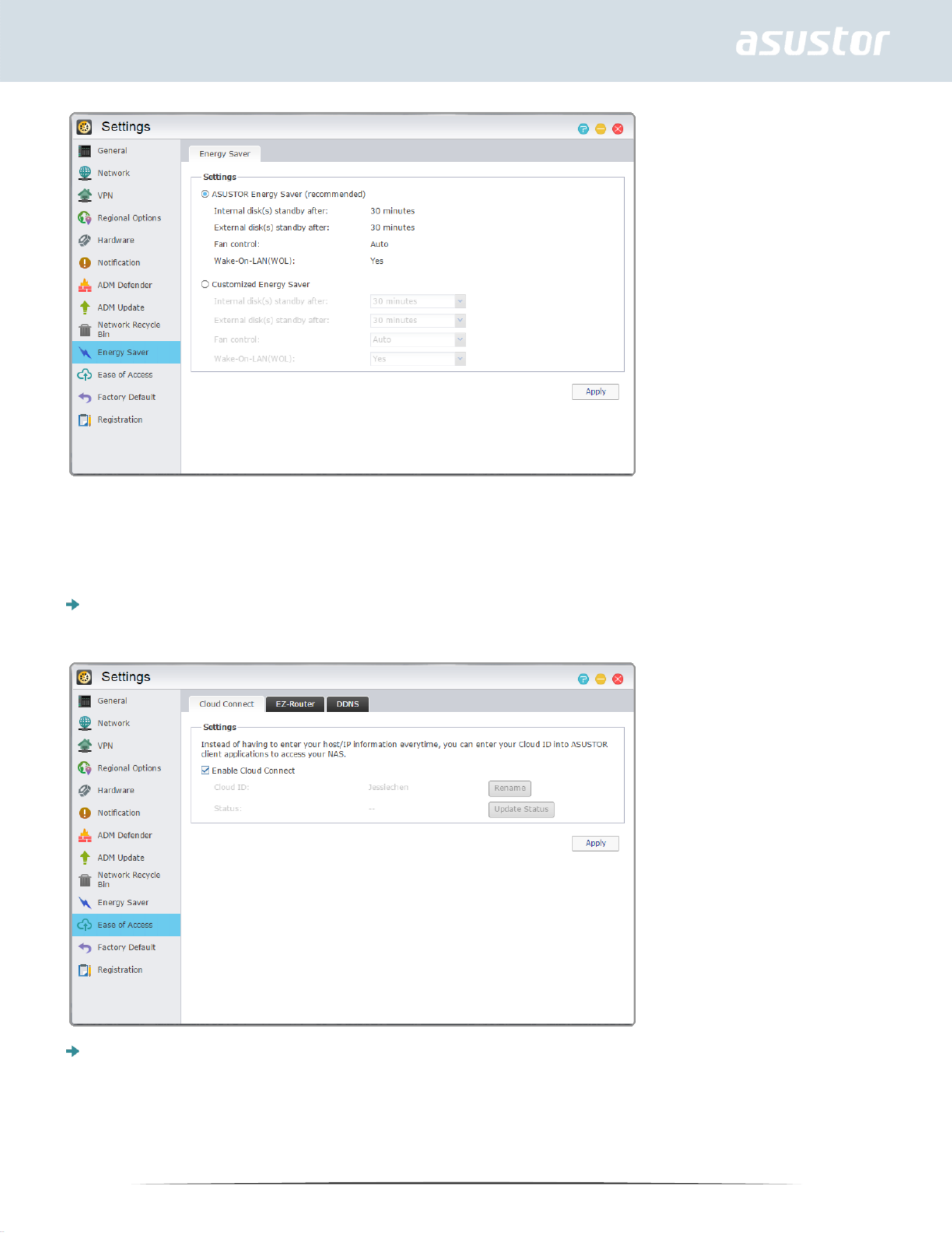
27
Ease of Access
Here you can configure all the necessary settings for remote access.
Cloud Connect: Here you can obtain a Cloud ID for your NAS. By entering the Cloud ID into
ASUSTOR client applications, you can access your NAS without having to enter the host/IP
information.
EZ-Router: Here you can set up your network router automatically for direct NAS access from any
device with Internet access.

28
Reminder: Your router must support UPnP/NAT-PMP. Please note that not all routers
support automatic configuration. Please see the hardware compatibility list found on the
ASUSTOR website for more information.
DDNS: Here you can create or configure your DDNS account. DDNS allows you to use a persistent
host name (i.e., nas.asustor.com) to connect to your NAS. You won’t have to worry about
remembering your NAS’s IP address. This feature is often used in dynamic IP environments.
See More
NAS 221 - Remote Access - Using Cloud Connect™
NAS 224 - Remote Access - Manual Configuration
Compatibility - EZ-Router
29
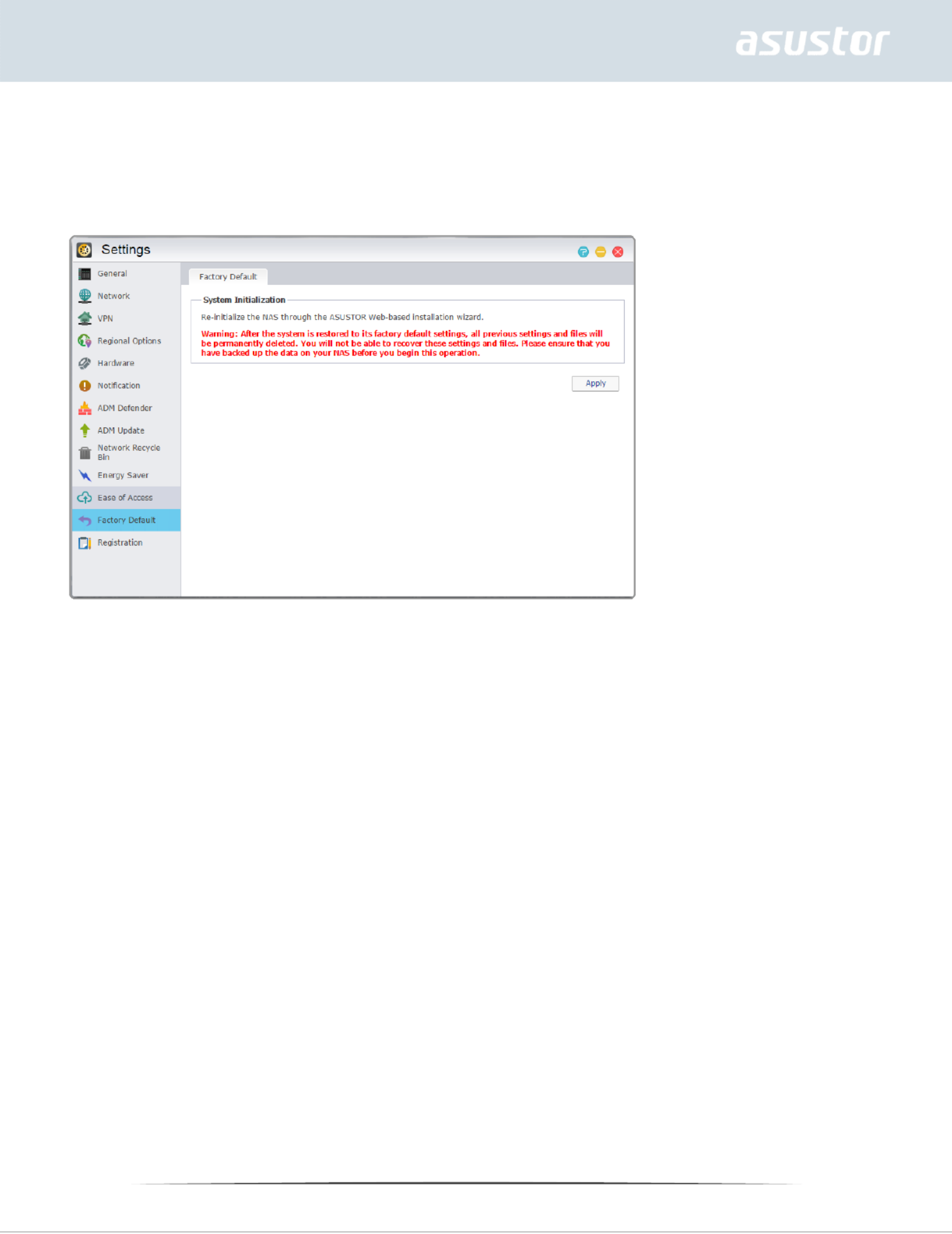
Factory Default
Here you can restore the system back to its factory default settings. After this, the system will return
to its pre-initialized state. For security reasons, you will be asked to enter the administrator password
before performing this operation. You can then initialize the system again through Control Center or
by logging into ADM.
Warning: After the system is restored to its factory default settings, all previous settings and
files will be permanently deleted. You will not be able to recover these settings and files.
Please ensure that you have backed up the data on your NAS before you begin this operation.
Registration
Here you can sign up for a personal account (ASUSTOR ID) and register your product. Once the
product has been registered, your ASUSTOR ID will be automatically enabled.

31
About Windows Active Directory
After successfully adding your NAS to your AD domain, you can then configure access rights using
the Domain Users, Domain Groups and Shared Folders settings found in the Access Control system
app (see section 3.4 Access Control). AD users can then use their own AD accounts to log in and
access the NAS.
S M EE ORE
NAS 102 - Introduction to File Transfer Protocols
NAS 106 – Using NAS with Microsoft Windows
NAS 206 – Using NAS with Windows Active Directory
Mac OS X
After enabling Mac OS X file service, you can access your NAS via any Mac OS X operating system
(i.e., Mac OS X v10.7). This file transfer protocol is called AFP (Apple Filing Protocol). You can also
use Time Machine to back up data to your NAS.
Apple Filing Protocol (AFP): This is the protocol used when transferring files between Mac OS X
and local area networks. Go to the Finder and click “Go” in the Finder menu, then select “Connect
to Server.” This will bring up the Connect to Server dialog box. Here you can enter the IP address
that you want to connect to.
For example afp://192.168.1.168 :
Bonjour Service Name: Your NAS will be identified by this name in the Finder.

32
Time Machine Support: Here you can enable Time Machine support and select the shared folder
that you wish to back up to. If multiple Mac users wish to access this feature simultaneously,
please see NAS 159 – Time Machine: Best Practice for guidance.
About Bonjour
Bonjour, also known as zero-configuration networking, has been widely used in Apple related
products. It will scan your vicinity for other Apple devices and then let you directly connect to them
without having to know their actual IP addresses.
After enabling this service, you will be able to see your NAS in the left hand panel of the Finder under
“Shared”. Simply click on your NAS to connect to it.
See More
NAS 102 - Introduction to File Transfer Protocols
NAS 108 – Using NAS with Apple Mac OS X
NAS 159 – Time Machine: Best Practice
NFS
After enabling NFS, you will be able to access your NAS via UNIX or Linux operating systems.

33
About NFS
After enabling NFS service, you can configure access rights using the Shared Folders setting found in
the Access Control system app (see section 3.4 Access Control). This option will be hidden if NFS
service has not been enabled.
See more
NAS 102 - Introduction to File Transfer Protocols
NAS 109 - Using NAS with Linux
FTP Server
After enabling the FTP server setting, you will be able to access your NAS via any FTP client program
(i.e., FileZilla). FTP server access rights are the same as those for the system (ADM). Should you
wish to change or configure these access rights, you may do so using the shared folders setting
found in the Access Control system app (see section 3.4 Access Control).
Unicode support: Please enable this option if your FTP client program supports Unicode.
Enable anonymous: Enabling this option will allow FTP client programs to access your NAS
anonymously, without the need for a username or password. For security reasons, this is not
recommended.

34
Enable SSL/TLS: Enable encryption for FTP connections.
Maximum number of all FTP connections: The maximum number of simultaneous FTP
connections allowed.
Maximum number of connections per IP: The maximum number of connections allowed per IP
or system.
Max upload rate: The maximum upload speed per connection. 0 represents no limitation.
Max download rate: The maximum download speed per connection. 0 represents no limitation.
Passive FTP: To minimize the security concerns of connecting from a server to a client, a type of
connection mode called Passive Mode (PASV) was developed. When a client program starts to
connect, it will notify the server to activate Passive Mode.

35
About Passive FTP
Passive mode FTP can be used to overcome the problem of active mode FTP being blocked by
Passive FTP makes the FTP client establish all connections to the FTP server, as opposed to firewalls.
the web host supplying the return port. Firewalls typically allow passive FTP connections without
requiring additional configuration information.
See More
NAS 102 - Introduction to File Transfer Protocols
WebDAV
After enabling WebDAV you can access your NAS via HTTP or HTTPS protocol by using a Web browser
or other client programs.
See More
NAS 102 - Introduction to File Transfer Protocols
NAS 208 – WebDAV: A Secure File Sharing Alternative to FTP
Web Server
ADM comes built-in with an independent web server (apache) that you can use to host your own
website. After enabling this feature, the system will create a shared folder called “Web” that will
serve as the web server’s root directory.

36
PHP register_globals: This feature is not enabled, by default. Enable this if a website program
specifically requests you to. Otherwise, it is recommended that you leave this feature disabled for
system security reasons.
Virtual Host: You can use this feature to simultaneously host several websites on your NAS.
See More
NAS 321 – Hosting Multiple Websites with a Virtual Host
MySQL Server

37
ADM comes pre-installed with MySQL, which you can use for website databases.
Reminder: You can manage your MySQL server with phpMyAdmin which can be downloaded
and installed from App Central.
Reset Password: If you happen to forget your MySQL login password, you can reset the
password for the “root” account (The default password is “admin”). This is also the default
administrator account.
Reinitialize Database: Here you can reinitialize your entire MySQL database. Upon
reinitialization, all of your MySQL databases will be erased.
About MySQL
For the MySQL administrator account, the default username is “root” and the default password is
“admin”. For security reasons, please remember to change the password for this account.
Terminal
You can enable SSH service if you wish to manage your NAS over Secure Shell (SSH). If you wish to
transfer data to your NAS through SFTP (Secure FTP) you can enable that here as well.
Note: For security reasons, SSH only allows the “admin” account or the “root” account to
log in. The passwords for both these accounts are identical.

38
Rsync Server
After enabling Rsync server, your NAS will become a backup server and will allow remote backup
from another ASUSTOR NAS or any other Rsync-compatible servers.
Enable Rsync server: If you wish to permit encrypted backup for clients, please enable support
for encrypted transmission via SSH. If you enable this feature the system will then automatically
enable SSH service (3.2.8 Terminal).
Manage Rysnc User: If you wish to create restrictions on the Rsync connections that can back up
to your NAS, please click on Manage Users to create different Rsync user accounts.
Reminder: Rsync accounts are different and independent from system accounts.
Add New Backup Modules: Click on Add to create a new backup module. Each backup module
will then correspond to a physical path within the system. When an Rsync client connects to your
NAS, it will be able to select a backup module. Data will then be backed up to the module’s
corresponding physical path.

39
See More
NAS 259 – Using Remote Sync (Rsync) to Protect Your Data
NAS 351 – Remote Sync (Rsync): Best Practice
TFTP Server
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is a simple type of file transfer protocol that is used to transfer
configurations or small files, providing no authentication.
40
TFTP root folder: Specifies the folder on the ASUSTOR NAS that TFTP clients can access.
TFTP client permission: Specifies the permissions for TFTP clients. If you select “Read Only”,
TFTP clients will only be able to view the contents of the TFTP root folder. If you select “Read &
Write”, TFTP clients will be able to modify the contents of the TFTP root folder.
Client connections allowed: Selecting “All Connections”, will allow all TFTP clients to connect to
the NAS. You can also choose to limit connections to TFTP clients from a specified range of IP
addresses.
Timeout: Here you can specify the timeout time which is used to terminate idle connections,
providing an additional later of security.
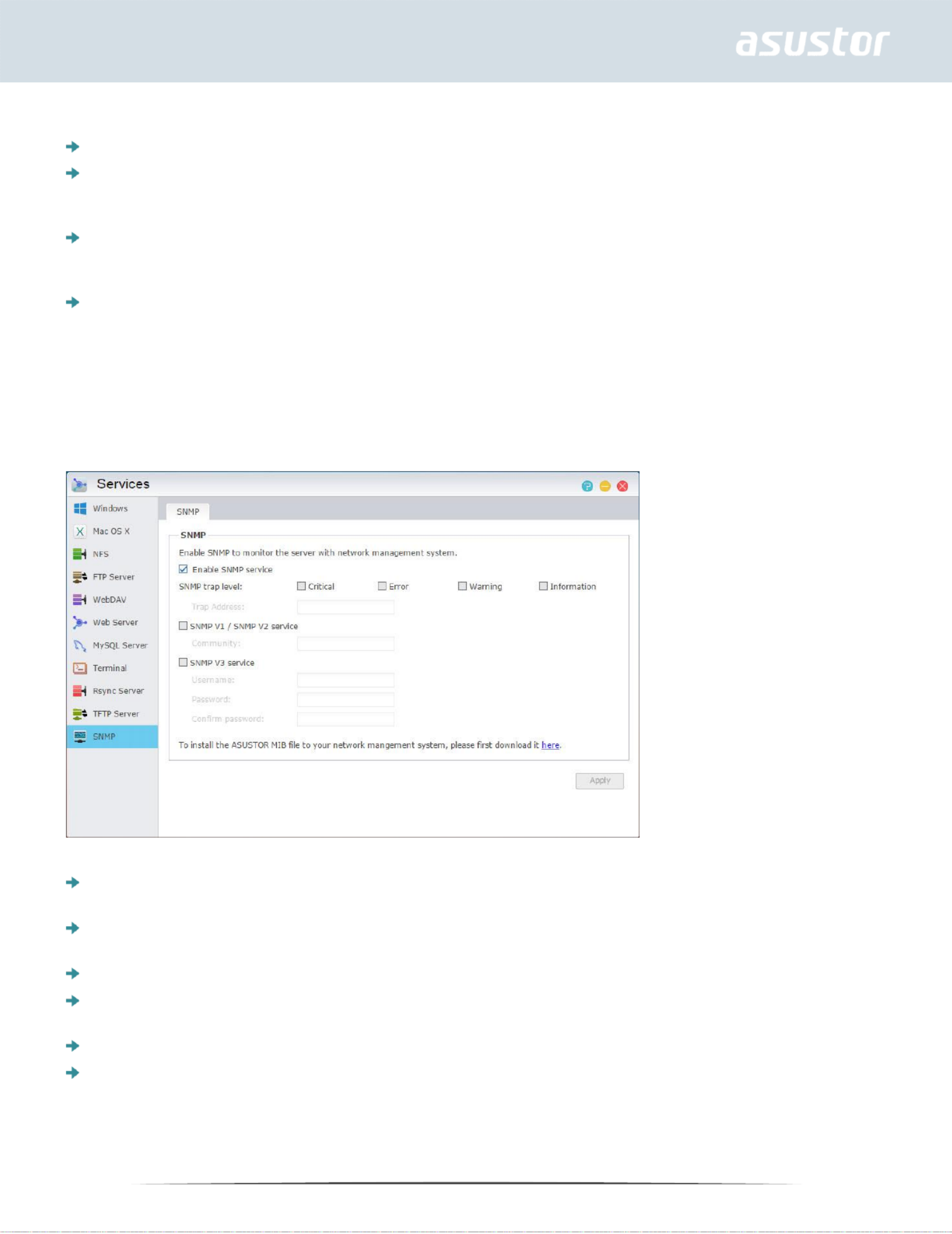
SNMP
Enabling SNMP allows users to use network management software to monitor the status of their
ASUSTOR NAS.
SNMP trap level: Here, you can configure SNMP trap to actively provide warning messages.
Warning event types include: Critical, Error, Warning and Information
Trap Address: After configuring the SNMP trap level please input the IP address of the network
management station (NMS) here.
SNMP V1 / SNMP V2 service: Selecting this checkbox will enable SNMP V1 / V2 service.
Community: Enter a community name here. Community names must include 1 to 64 displayable
characters and may not include the following characters: “ ‘ \ and blank spaces.
SNMP V3 service: Selecting this checkbox will enable SNMP V3 service.
Username: Please input the SNMP V3 username here. This username must include 1 to 64
displayable characters and may not include the following characters: “ ‘ \ and blank spaces.

41
Password: Please input the corresponding password for the SNMP V3 username in the field above.
Letters in the password are case-sensitive. You may input 8 to 127 displayable characters
including letters from the English alphabet, numbers and symbols. The password may not include
the following characters: “ ‘ \ and blank spaces.
See More
NAS 271 - ASUSTOR NAS MIB Guide
Storage Manager
Volume
Note: This function may differ depending on the NAS model in use.
Storage space on your NAS consists of logical volumes which are made up of a single disk or multiple
disks combined together. Here you can set up new storage space for your NAS and, according to
your data protection needs, select the most suitable RAID level. In order to maintain data integrity,
you may only use internal disks when creating storage space for your NAS. ADM does not support the
use of external disks for storage space.
Reminder: The RAID levels that you may employ will depend on your NAS product model and
the number of disks that you are using.
When setting up new storage space, ADM offers the following two options:
Quick Setup: You need only specify the requirements for the storage space (i.e., you wish to
have a higher level of data protection). Based on this and the number of disks you have, ADM will
automatically create a storage volume and select an appropriate RAID level for it.

42
Advanced Setup: Based on the current number of disks, you can manually select a RAID level or
set up a spare disk.
Reminder: In order to optimize disk space utilization, it is recommended that you use disks
of the same size when creating storage space.
About RAID
In order to provide optimal storage space utilization and data protection, ADM supports multiple
RAID levels allowing you to select the appropriate level for your needs. The following volume types
levels are all supported by ADM:
Non-RAID Volume Types
Single: Only uses a single disk in the creation of storage space. This configuration does not offer any
type of data protection.
JBOD: An acronym for “just a bunch of disks”, JBOD uses a combination of two or more disks to
create storage space. The total storage capacity is the capacities of all the disks added together. The
advantage of this configuration is that it allows you to use different sized disks together and provides
a large amount of storage space. The downside is that it does not offer any sort of data protection.
RAID Volume Types
RAID 0: Uses a combination of two or more disks to create storage space. The total storage capacity
is the capacities of all the disks added together. The advantage of this configuration is that it allows
you to use different sized disks together and provides a large amount of storage space. Also, data in
RAID 0 volumes is accessed in parallel which provides improved performance. The downside is that
RAID 0 does not offer any sort of data protection.
RAID 1: In RAID 1 your data is written identically on two disks, thereby producing a “mirrored set”.
Exactly the same data is stored on the two disks at all times. RAID 1 protects your data from loss
should one of your disks fail. RAID 1’s advantage is that it offers protection for your data by
providing data redundancy. The downside of this configuration is that when combining two disks of
differing sizes, the total storage space will be equal to the size of the smaller disk. Therefore, you will
be unable to use a portion of the larger disk.
Total available storage space = (size of smaller disk) * (1)
RAID 5: Combines three or more disks to create a storage space that is able to support one failed
disk. Should one of your disks fail, your data will still be protected from loss. In the event of disk
failure, simply replace the failed disk with a new one. The new disk will automatically be
accommodated into the RAID 5 configuration. The advantage of using RAID 5 is that is that it
provides data protection through data redundancy. The downside to using RAID 5 is that when
combining disks of differing sizes, the total storage space will be calculated based on the size of the
smallest disk.
Total available storage space = (size of smallest disk) * (total number of disks –1)

43
RAID 6: Combines four of more disks to create a storage space that is able to support two failed
disks. Should two of your disks fail, your data will still be protected from loss. In the event of disk
failure, simply replace the failed disks with new ones. The new disks will automatically be
accommodated into the RAID 6 configuration. The advantage of using RAID 6 is that it is able to
provide superior data protection through data redundancy. The downside to using RAID 6 is that
when combining disks of differing sizes, the total storage space will be calculated based on the size of
the smallest disk.
Total available storage space = (size of smallest disk) * (total number of disks –2)
RAID 10 (1+0): Combines four or more disk to create a storage space that is able to support
multiple failed disks (as long as the failed disks do not belong to the same “mirrored set”). RAID 10
provides the data protection of RAID 1 along with the access efficiency of RAID 0. With respect to
data protection, RAID 10 uses the RAID 1 method of having the exact same data written identically
on two disks, producing “mirrored sets”. These “mirrored sets” are then combined together in a RAID
0 configuration. RAID 10 requires an even number of four or more disks. When combining disks of
differing sizes, the total storage space will be calculated based on the size of the smallest disk.
Total available storage space = (size of smallest disk) * (total number of disks / 2)
About D Trim SS
Enable SSD Trim allows the SSDs installed on the NAS to maintain stable read/write performance
while simultaneously controlling the frequency of overwriting to specific blocks, extending the life of
SSDs.
Note:
The function is only available on the following models: AS-6/50/51/61/62/70 series.
When using an SSD in a Single, JBOD, or RAID 0/1/10 volume configuration, the Trim command
for it will be enabled automatically.
The Trim feature under RAID 5 and 6 configurations can only be enabled on the SSDs with DZAT
(Deterministic Read Zero after TRIM) support. Please contact your SSD manufacturers for details
on DZAT support.
See More
NAS 251 – Introduction to RAID
NAS 352 – Online RAID Level Migration and Capacity Expansion
Disk
Here you can check on the status of all your disks. You can also inspect their S.M.A.R.T. information
and conduct tests on your disks.

44
S.M.A.R.T. Info: S.M.A.R.T. is an acronym for Self-Monitoring Analysis and Report Technology. It
is a type of self-monitoring mechanism for disks that detects and reports on various indicators of
reliability, with the hope of anticipating failures.
Disk Doctor: Here you can check your disks for bad sectors or conduct S.M.A.R.T. tests.

45
iSCSI
iSCSI is a type of network storage technology that offers high expandability and low implementation
costs. Through existing network infrastructure and iSCSI you can use your NAS to expand existing
storage space or have it act as a backup destination. iSCSI consists of two ends, a target and an
initiator. The initiator is used to search for iSCSI hosts and to set up targets.
IQN: IQN (iSCSI Qualified Name) is the unique name for each iSCSI target. This name should not
be the same as any of the other target IQNs on other hosts.

46
CHAP Authentication: CHAP authentication can be used to verify a user’s identity. If you
choose to use CHAP authentication, a CHAP password must first be entered from the initiator for
verification before it can connect to the target.
Mutual CHAP Authentication: Mutual CHAP authentication requires both the target and the
initiator to have usernames and passwords. When establishing a connection, the target and the
initiator will have to authenticate each other using their respective credentials.
LUN Pool: Here you can check on the status of all iSCSI LUNs and assign corresponding iSCSI
targets.
iSNS Server: iSNS (Internet Storage Name Service) iSCSI management. Here, you can register
iSCSI targets with the iSNS Server, for convenient centralized management.
See More
NAS 308 – Introduction to iSCSI
iSCSI LUN
This tab allows you to create/remove, mount/unmount iSCSI LUNs, and create/manage LUN
snapshots.
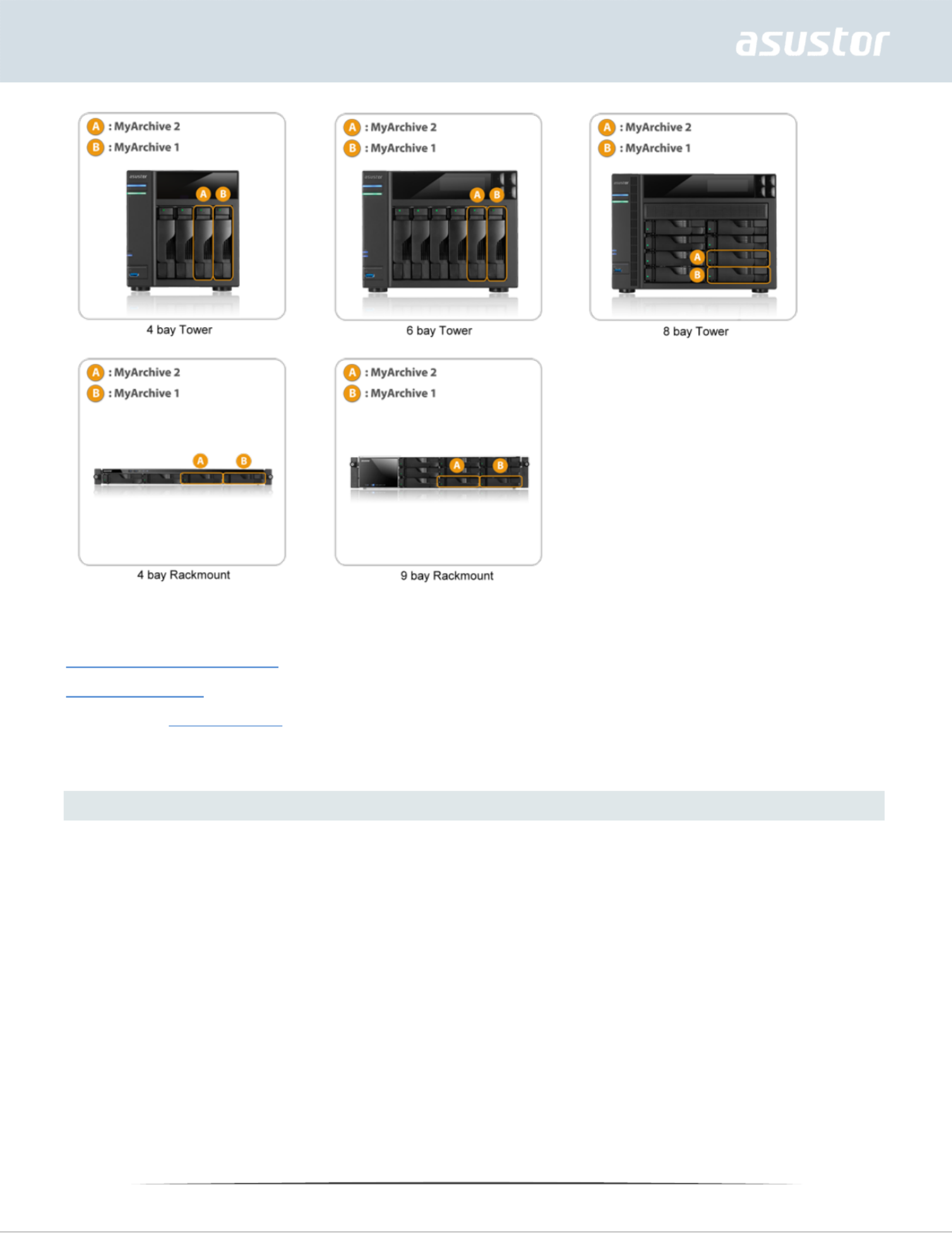
MyArchive
Note: This function may differ depending on the NAS model in use.

47
MyArchive is a function designed especially for data management and sharing, giving you added
flexibility when using multiple hard disks for data backup or exchange. When MyArchive hard disks
have been inserted into the MyArchive disk bay, you will immediately be able to access the data on
the hard disk.
MyArchive Hard Disk: Users will need to first convert hard disks into MyArchive hard disks
before being able to use the MyArchive function.
MyArchive Disk Bay: Located in the last one or two disk bays, towards the right side of the NAS
(the number and position of the disk bays will depend on the model in use). If you wish to use the
MyArchive function please remember to first leave a MyArchive disk bay empty.
2-bay NAS models will have one allocated MyArchive disk bay.
4-bay NAS models and up will have two allocated MyArchive disk bays.
48
See More
NAS 255 – Using MyArchive
Video - MyArchive
Accessories: Hard Disk Tray
Access Control
Local Users
Here you can manage (add, edit or remove) the local users in the system and assign their access
rights to shared folders.

50
Reminder: If you have a relatively large number of users on the system, you can
conveniently assign access rights by user group instead of assigning access rights for each
user one by one.
Within ADM, a single user’s access rights with regards to shared folders will depend on the user’s
existing access rights and on the access rights of the group that the user belongs to. Both sets of
access rights will be checked against each other in order to determine priority (please see Appendix
7.1). For convenience, the system provides a preview mode which allows you to first preview any
changes that you make to access rights.
About Local Groups
After initialization, the system will automatically create two user groups, “administrators” and “users”.
“administrators” is the default administrator group. If a user is added to this group, they will possess
a majority of the administrator access rights. The “admin” account belongs to the “administrators”
group by default and cannot be removed from it.
See More
Appendix 7.1 – Permission Mapping Table
Domain Users
Here you can view all AD user accounts and manage their access rights to shared folders once your
NAS has been successfully added to an AD domain.

51
Reminder: ASUSTOR NAS can support more than 200,000 AD users and groups. When
joining an AD domain for the first time, depending on the number of users and groups, it
may take a while for all of them to become visible.
See More
Appendix 7.1 – Permission Mapping Table
Domain Groups
Here you can view all AD user groups and manage their access rights to shared folders once your
NAS has been successfully added to an AD domain.
Reminder: ASUSTOR NAS can support more than 200,000 AD users and groups. When
joining an AD domain for the first time, depending on the number of users and groups, it
may take a while for all of them to become visible.

52
See More
Appendix 7.1 – Permission Mapping Table
Shared Folders
Here you can manage your shared folders and set up their access rights in relation to users and user
groups. Shared folders allow your NAS to become a file server. They are fundamental in sharing files
with the outside world. Consequently, correctly setting up their access rights is very important in the
management of your data.

53
Invisible in “Network” or “My Network Places”: This setting only applies if you are using
Microsoft Windows. When you enable this setting, your NAS will cease to automatically appear in
“Network” or in “My Network Places”. Please note that enabling this setting will not affect the
connection to your NAS in any way.
Empty Recycle Bin: Click this button to empty all contents in this shared folder’s Recycle Bin
immediately.
Encrypt this shared folder: Here you can choose whether or not you want to encrypt your
shared folder and whether or not you want to auto-mount it at system startup. Should you choose
to encrypt your folder, after the system restarts, you will have to manually enter the password or
import the encryption key for the folder in order to access it. Encrypted folders are normally used

54
for the storage of critical or confidential data. Should you lose your NAS you still needn’t worry
about your data leaking out and falling into the wrong hands.
Convert to the new ASUSTOR encryption mechanism: This option will only appear under
“ ” ’Edit for encrypted folders that have been encrypted using ASUSTOR s previous encryption
mechanism. Converting to the new encryption mechanism will require extra volume space in order
to temporarily store all the files originally in the folder. This required space is the total capacity of
all the files in the shared folder.
Export/import encrypted key: Selecting Export encrypted key will download the encrypted “ ”
key to your computer. When you need to mount an encrypted folder, you can select Enter “
Password Import encrypted key to mount the shared folder and begin accessing it.”or “ ”
Reminder: You can choose to enable or disable encryption for folders even after they have
been created. Encryption is available for use with all shared folders and is not just limited to
system default folders. The access speed for encrypted folders will normally be slower than
for unencrypted folders.
Warning:
1. When choosing to use encrypted shared folders, please make it a point to remember your
password. Should you forget your password, the data in the shared folder will become
unrecoverable.
2. Older versions of ADM are unable to read the contents of shared folder encrypted using
the new encryption mechanism introduced in ADM 2.4.0. If you wish to downgrade your
firmware to 2.3.1 or an older version, please first decrypt any shared folders that have
been encrypted using the new encryption mechanism before you begin downgrading.
NFS Privileges: Here you can set NFS privileges for individual folders after first enabling NFS
service.

55
About Shared Folders
After initialization, the system will automatically create a shared folder “public”. By default, all users
can access the files in this folder. Additionally, the system will automatically create a personal folder
for each user (using the user’s account name) that by default, can only be accessed by the
mentioned user.
Windows ACL: Here you can choose to enable or disable Windows ACL for specified shared
folders.

56
About Windows ACL
1. After enabling Windows ACL for a shared folder, the shared folder and all subfolders and files
contained within it can be assigned user or group permissions.
2. The following shared folders do not support Windows ACL permissions: Home, User Homes,
PhotoGallery, Web, Surveillance, MyArchive, Network Recycle Bin, virtual devices, external devices
(USB hard drives, optical drives).
3. After enabling Windows ACL you will be able to use ADM’s File Explorer or Microsoft Windows
Explorer to configure permissions. After disabling Windows ACL you will only be able to configure
permissions from within ADM’s File Explorer.
4. If you enable Windows ACL and then later decide to disable it, all file and folders will be re-
assigned with Read & Write permissions for all users.
5. No matter if you are using Windows ACL or not, users will still require shared folder and file
permissions in order to access files.
Folder Access Rights: –Shared folders access rights are the first level of access rights that will
be examined. You can edit them here.
See More
Appendix 7.1 – Permission Mapping Table
Virtual Drive
You can mount an ISO image file (.iso file) as a virtual drive and directly browse the content of the
ISO image file. ADM’s virtual drive function also provides simplified access control settings allowing
you to either configure access for all users or limit access to only administrators.

57
App Privileges
Here you can configure the users’ or user groups’ access rights to apps. For example, if a particular
user’s account is denied access to the Surveillance Center app, once he/she logs in, he/she will not
be able to see the Surveillance Center app icon on their ADM home screen. The user will have no way
of opening or accessing the app.
Web applications may be public in nature (i.e., WordPress) or have their own account
management systems (i.e., Joomla). Therefore, there is no way to restrict access to them through
ADM.
With regards to domain users, the system only offers the option of setting their File Explorer
access rights.

58
Backup & Restore
Remote Sync
Remote Sync (Rsync) can allow your NAS to be used as a backup destination or backup source.
When using your NAS as a backup source, you can choose to back up the data from your NAS onto
another remote ASUSTOR NAS or Rsync compatible server. When your NAS acts as a backup
destination, you can back up the data from another remote ASUSTOR NAS or Rsync compatible
server onto your NAS.
Use encrypted transmission: If you choose to use encrypted transmission, you will have to
enter the other host’s SSH connection information in addition to your Rsync account information.
Use 1 on 1 folder synchronization: If you decide to use 1 on 1 folder synchronization, all the
data in the designated destination folder will be synchronized with the data in your source folder
(you may only select one folder). The contents of both folders will be exactly the same. If you
decide not to use this feature, all your chosen source folders (you may select multiple folders) will
be copied one by one to the destination folder.
Keep extra files at the destination: Once the copying and synchronization of files is completed,
the data at the source and destination should be exactly the same. However, sometimes there are
extra files present at the destination. These files are only present at the destination but not at the
source. By enabling this option, these extra files will be kept at the destination and will remain
untouched.
Archive mode (incremental backup): After enabling this feature, successive backup jobs (after
your first backup job) will only copy the data that has changed since your last backup job (block
level). For example, if you have made some small changes to a 10 MB file, incremental backup will
only copy the portions that you have made changes to. This can significantly reduce bandwidth
usage.
Compress data during the transfer: During backup you can compress the data that is being
transferred thereby lowering bandwidth usage.
Keep file metadata: When you enable this option, certain file properties (permissions, extensions,
attributes, owner, groups, etc.) will be sent along with the file to the destination.
59
Support sparse files replication: You will only need to enable this option when the data that
you wish to back up contains sparse files. Normally, you will not have to enable this option.
Mission Mode: Sometimes backup jobs may be stopped because of various connection problems
with a busy server on the other end. ASUSTOR’s Mission Mode option allows you to configure the
number of connection attempts and time interval for connection attempts, ensuring for the
successful completion of your backup job. This also gives IT administrators a significant amount of
flexibility when configuring backup jobs.
Reminder: If you wish to use Remote Sync while using your NAS in conjunction with another
remote ASUSTOR NAS, please remember to enable the Rsync server feature on the remote
NAS (Services -> Rsync Server). For more information please see 3.2.9 Rsync Server.
See More
NAS 259 – Using Remote Sync (Rsync) to Protect Your Data
NAS 351 – Remote Sync (Rsync): Best Practice
FTP Backup
FTP backup can allow for your NAS to be used as a backup destination or backup source. When using
your NAS as a backup source, you can choose to back up the data from your NAS onto another
remote ASUSTOR NAS or FTP server. When your NAS acts as a backup destination, you can back up
the data from another remote ASUSTOR NAS or FTP server onto your NAS.
Mission Mode: Sometimes backup jobs may be stopped because of various connection problems
with a busy server on the other end. ASUSTOR’s Mission Mode option allows you to configure the
number of connection attempts and time interval for connection attempts, ensuring for the
successful completion of your backup job.
Reminder: If you wish to use FTP backup while using your NAS in conjunction with another
remote ASUSTOR NAS, please remember to enable the FTP server feature on the remote NAS
(Services -> FTP Server). For more information please see 3.2.4 FTP Server.

60
About FTP Backup
Normally, FTP backup is suitable for use with a majority of FTP servers. However, incompatibility
issues do arise from time to time. Therefore, it is recommended that you use two ASUSTOR NAS
units to execute your backup jobs.
See More
NAS 257 - FTP Backup
Cloud Backup
Note: This function may differ depending on the NAS model in use.
Using Cloud Backup, you can schedule regular backups of your NAS data to a cloud storage space or
back up the data from a cloud storage space onto your NAS. Currently supported cloud storage
services are as follows:
Amazon S3
Mission Mode: Sometimes backup jobs may be stopped because of various connection problems
with a busy server on the other end. ASUSTOR’s Mission Mode option allows you to configure the
number of connection attempts and time interval for connection attempts, ensuring for the
successful completion of your backup job.
See More
NAS 254 – Cloud Backup
Internal Backup

61
Internal Backup allows you to backup data from NAS to local shared folders. Using Internal Backup
with MyArchive disks creates a perfect off-site backup solution.
Use 1 on 1 folder synchronization: If you decide to use 1 on 1 folder synchronization, all the
data in the designated destination folder will be synchronized with the data in your source folder
(you may only select one folder). The contents of both folders will be exactly the same. If you
decide not to use this feature, all your chosen source folders (you may select multiple folders) will
be copied one by one to the destination folder.
Preferred file permission for all users at the destination: If the ACL status of the source and
destination are not the same, this permission setting will be applied to the files at the destination.
Keep owner: By default, the owner of the files at the destination will be the user who created the
backup job. Enabling this option can allow you to maintain the original ownership of the files at the
destination.
Support sparse files replication: You will only need to enable this option when the data that
you wish to back up contains sparse files. Normally, you will not have to enable this option.
External Backup
Here you can choose to backup data from USB or eSATA external hard disks to your NAS or backup
data from your NAS to these external hard disks. In addition to supporting two-way backup, this
feature also supports scheduled backups, making sure that your data is always backed up.
Mission Mode: Sometimes backup jobs may be stopped because of various connection problems
with a busy server on the other end. ASUSTOR’s Mission Mode option for external backup allows
you to configure the time interval for connection attempts, ensuring for the successful completion
of your backup job. This also gives IT administrators a significant amount of flexibility when
configuring backup jobs.

63
About One Touch Backup
Once the USB backup button is held down for 1.5 seconds, One Touch Backup will be triggered.
During the backup process, the USB backup LED indicator light will blink continuously. After the
backup process has finished, the light will cease to blink and will then return to its previous state. If
you wish to disable One Touch Backup, you can adjust the settings accordingly.
System Settings
Here you can export or restore system settings in .bak format (file extension). This feature also
supports scheduled backup, which means that you can create scheduled backup jobs and then export
the settings to a specified location on your NAS.
65
External Devices
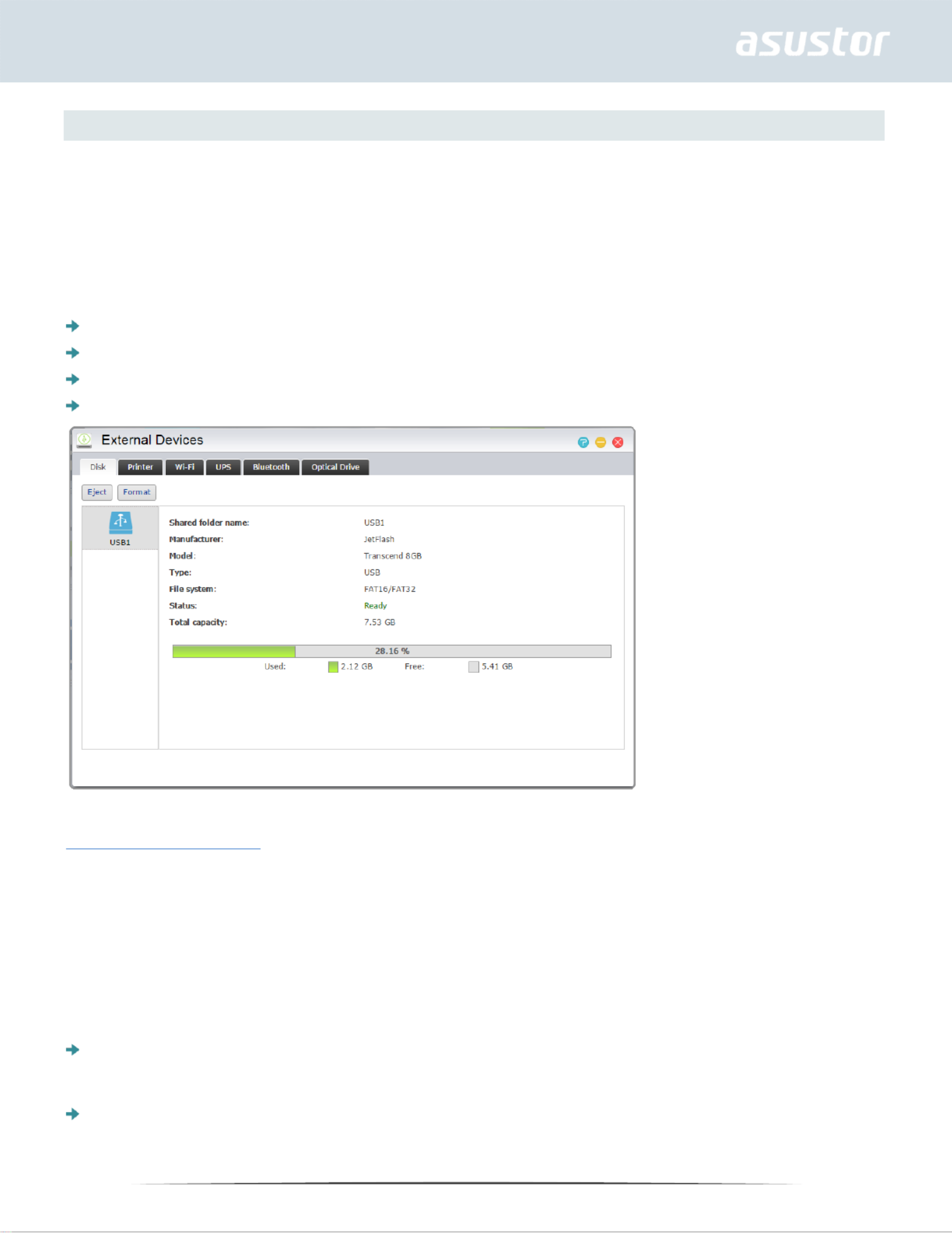
Disk
Here you can view and format all USB or eSATA external hard disks that are connected to your NAS.
Supported file systems are as follows:
Reminder: If your device cannot be detected, please try connecting again using another
cable or port.
FAT32: for use with Windows and Mac OS X
NTFS: for use with Windows
HFS+: for use with Mac OS X
EXT4: for use with Linux
See More
Compatibility – Hard Disk
Printer
Here you can view all the USB printers that are connected to your NAS and their respective printing
logs. Additionally, ASUSTOR NAS also supports Apple AirPrint.
Reminder: ASUSTOR NAS supports up to three USB printers.
Management: Here you can activate and configure device names for AirPrint. You can send
printing instructions from your Apple mobile device to your printer when they are part of the same
local area network as your NAS.
Clear All Waiting Jobs: Here you can choose to cancel all waiting print jobs.
66
See More
Compatibility – USB Printer
Wi- Fi
After connecting your USB Wi-Fi adapter to your NAS, you can view its detailed information here.
About Using Wi-Fi with your NAS

67
If you wish to use Wi-Fi with your NAS, please take a look at the compatibility list on the ASUSTOR
website before purchasing a Wi-Fi adapter. Wi-Fi signal strength and stability will vary according to
the hardware that you are using (e.g., Wi-Fi network card and wireless access point) and any
physical barriers that are present. Therefore, ASUSTOR has no way of guaranteeing Wi-Fi signal
strength or stability. For best results, a wired Ethernet connection is recommended.
See More
Compatibility – USB WiFi Dongle
UPS
A UPS can provide backup power to your NAS in the event of a power outage. Using a UPS can
protect your data and NAS from sudden shutdown or service interruptions.
Network UPS: Here you can setup your NAS to be the network UPS server (Master mode) and
set its IP address, when the UPS’s USB cable is connected to your NAS. Other devices that are in
the same local area network will be then set to slave mode. In the event of a power outage, the
master and slave devices will immediately detect this stoppage in power and then determine
whether or not to commence shutdown procedures based on the time period that has been set.
Shut down: When the NAS receives notification of a power outage from the UPS, it will begin
normal shutdown procedures.
Safe mode: When the NAS receives notification of a power outage from the UPS, it will stop all
services in accordance with normal procedures and unmount all storage volumes. If you have
enabled the "In the event of a power outage, enable the NAS to return to its previous state once
power has been restored" setting (configurable via Settings Hardware Power), once the NAS → →
has been shut down under safe mode, it will automatically turn on once power has been restored.
(This function is available for use with AS-6/7 series devices).

68
Reminder: When the NAS is configured as the network UPS server (Master mode), the
default username is “admin” and the password is “11111” when connecting to the network
UPS server.
See More
Compatibility - UPS
Bluetooth Devices
After you have connected your Bluetooth device to the NAS, you will be able to view its detailed
information here.
See More
Compatibility – Bluetooth
External Optical Drive
After connecting an external optical drive (CD, DVD, Blu-ray) to your NAS via USB, you can use File
Explorer to directly access any files that you have backed up to optical media and even transfer files
from your optical media to your NAS via drag and drop for future access.

69
About Using External Optical Drives with your NAS
This function only provides data access and does not support the audio and video playback of optical
media.
Certain optical drives will require additional power in order to operate properly. If you find that your
optical drive is not spinning or reading correctly, please use a USB Y-cable to add additional power.
See More
Compatibility – External Optical Drive
System Information
About This NAS
Here you can view general information about your NAS such as the hardware model number,
software version, BIOS version and present state of the system.

70
Network
Here you can review information about your network settings (i.e., IP address and MAC address).
Log
Here you can review logs of all system events. These logs include the system log, connection log and
file access log. ASUSTOR NAS also supports Syslog. This can allow you to employ centralized
management by sending your system event information to a Syslog server.
System log:
:
:
::All log entries about system events

71
Connection log:
:
:
::All log entries about system connections.
File access log:
:
:
::All log entries about file access.
Online Users
Here you can view the users that are currently logged in to ADM or any users that are using other
transfer protocols to connect to your NAS.
About Online Users
ADM is able to display any users who connect to your NAS using the following methods:

72
ADM system login (HTTP & HTTPS)
Windows File Service (CIFS/SAMBA)
Apple Filing Protocol (AFP)
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Secure Shell (SSH)
iSCSI
WebDAV
Dr. ASUSTOR
Dr. ASUSTOR performs checkups based the current state of your system, settings and connectivity.
After performing these checkups, Dr. ASUSTOR will diagnose any problems and provide you with
appropriate recommendations. Additionally, you can also export a health record for your NAS in order
to help ASUSTOR engineers quickly identify the causes of any problems. The health record contains
information pertaining to the NAS’s system event logs, core information and basic configuration files.
Activity Monitor
Note: This function may differ depending on the NAS model in use.
Activity Monitor dynamically monitors your NAS. Here you can view current usage information such
as:
CPU Usage
Memory (RAM) Usage
Network Traffic
Storage Space Usage
Resources Being Used by System Programs

73
File Explorer
File Explorer comes pre-installed with ADM and can be used to browse and manage the files on your
NAS. File Explorer displays accessible directories to users based on the access rights that are
assigned to them. Additionally, ADM supports three simultaneously open File Explorer windows. You
can easily make copies of files by dragging and dropping them into a different File Explorer window.
ISO Mounting: You no longer need to burn ISO files onto CDs in order to read them. Now you
can select ISO files from your NAS and directly mount them to shared folders (“read only” access
rights). You can then use your computer to access and read them. Later, when you are finished
with the files, simply unmounts them.
Share Link: You can use Share Links to share files with people who don’t have accounts on your
NAS. Share Links allow you to instantly create download links for designated files that you want to
share. Expiry dates can also be set for each Share Link that you create, allowing for safe and
flexible management.

74
Permissions: Right-clicking on a file or folder and then selecting “Properties” followed by the
“Permissions” tab will allow you to configure detailed access permissions for the file or folder.
If the top-level shared folder does not have Windows ACL enabled, the options for configuring
permissions will be:
Owner: The owner of the folder or file
Group: The group that has been assigned to the folder or file
Others: All other users on the system or network that are not owners or part of the group that
has been assigned to the folder or file.
The permission types that you will be able to configure are: RW (Read & Write), RO (Read Only)
and DA (Deny Access).
If the top-level shared folder has Windows ACL enabled, you will be able to configure file
permissions for all users and groups. In total, there will be 13 types of configurable permissions.
These types of permissions are as follows:
Reminder: An individual file or folder can utilize up to a maximum of 250 Windows ACL
permissions (including inherited permissions).
Traverse folder / execute file
List folder / read data
Read attributes
Read extended attributes
Create files / write data
Create folders / append data
Write attributes
Write extended attributes
Delete
Delete subfolders and files
Read permissions
Change permissions
Take ownership
Include inheritable permissions from this object’s parent: This option is enabled by default. The
system will automatically configure sub folders and files to inherit permissions from the object
above it. Disabling this option will reject all inheritable permissions and only keep newly added
permissions.
Replace all child object permissions with inheritable permissions from this object: Enabling this
option will replace all sub folder and file permissions with ones from the parent object.

75
Effective Permissions: Clicking on this button and then selecting a user from the list will allow you
to view the user’s effective permissions with regards to the specified folder or file.
My Computer: My Computer allows you to use File Explorer to browse the files on your local
computer. This allows you to use to use the File Explorer interface to manage all the files stored
on your NAS and local computer.
Task Monitor: Task Monitor allows you to view the progress, speed and status of downloads and
uploads. Additionally, Task Monitor’s multitasking and background operation allow you to
simultaneously upload and download multiple files. You no longer need to wait for tasks to be
completed one by one.
Java allows File Explorer to browse data on the local computer as well as proving support for the
dragging and dropping of files to File Explorer which are then uploaded to the NAS. Please install
Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 5 or later versions.
External Optical Drive: After connecting an external optical drive (CD, DVD, Blu-ray) to your
NAS via USB, you can use File Explorer to directly access any files that you have backed up to
optical media and even transfer files from your optical media to your NAS via drag and drop for
future access.
Note:
1. This function only provides data access and does not support the audio and video
playback of optical media.
2. Certain optical drives will require additional power in order to operate properly. If you
find that your optical drive is not spinning or reading correctly, please use a USB Y-cable
to add additional power.
Virtual Drive: You can mount an ISO image file (.iso file) as a virtual drive and directly browse
the content of the ISO image file. ADM’s virtual drive function also provides simplified access
control settings allowing you to either configure access for all users or limit access to only
administrators.
Network Recycle Bin: Here you can access the enabled Network Recycle Bins of all shared
folders.
Reminder: Currently, File Explorer can only show up to the first 10000 files contained within
folders.
F Explorer TP
FTP Explorer is ADM’s built-in FTP client. It can be used to connect to different FTP servers and
execute direct file transfers. This increases transfer efficiency as the file transfer process does not
require the use of any computers. FTP Explorer supports the following functions:
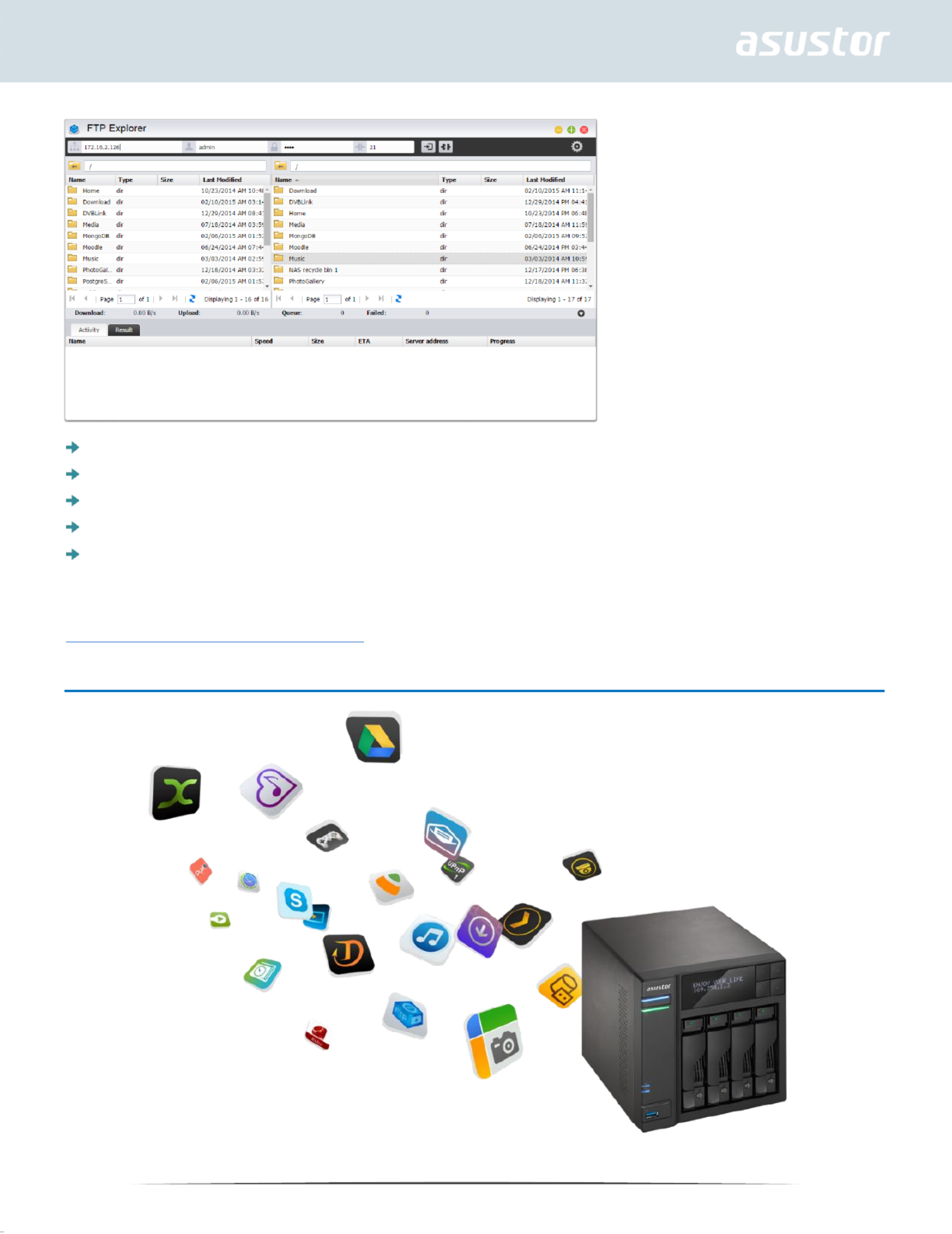
76
Site management, allowing you to configure multiple sets of FTP server connection information
Drag and drop file transfers
Encrypted transmission protocols (SSL/TLS)
Resuming downloads
Custom transfer speeds
See More
NAS 225 - Introduction to FTP Explorer
From App Central 4.
Produkt Specifikationer
| Mærke: | Asustor |
| Kategori: | I DEN |
| Model: | AS5102T |
Har du brug for hjælp?
Hvis du har brug for hjælp til Asustor AS5102T stil et spørgsmål nedenfor, og andre brugere vil svare dig
I DEN Asustor Manualer

9 Oktober 2024

10 August 2024

9 August 2024

3 August 2024

3 August 2024

1 August 2024

31 Juli 2024

25 Juli 2024

18 Juli 2024

15 Juli 2024
I DEN Manualer
- I DEN QNAP
- I DEN Samsung
- I DEN LG
- I DEN Apple
- I DEN HP
- I DEN D-Link
- I DEN Asus
- I DEN Toshiba
- I DEN Abus
- I DEN Buffalo
- I DEN Medion
- I DEN Seagate
- I DEN Netgear
- I DEN Western Digital
- I DEN Dell
- I DEN Mustang
- I DEN ZyXEL
- I DEN Synology
- I DEN Sandisk
- I DEN LaCie
- I DEN Veritas
- I DEN Promise Technology
- I DEN Sitecom
- I DEN Allnet
- I DEN Maxdata
- I DEN IoSafe
- I DEN CRU
- I DEN Approx
- I DEN Raidsonic
- I DEN Infortrend
- I DEN Origin Storage
Nyeste I DEN Manualer

23 Januar 2025

23 Januar 2025

23 Januar 2025

23 Januar 2025

12 Januar 2025

14 Oktober 2024

10 Oktober 2024

6 Oktober 2024

2 Oktober 2024

18 September 2024